
Out of these 5 d orbitals, the shapes of the first 4 d – orbitals are similar to each other which are comparatively different from the dz2 orbital whereas the energy of all 5 d – orbitals is same. For which we can say that there are 5 d – orbitals which are designated as d xy, d yz, d zx, d\( _\). Magnetic orbital quantum number for d orbitals is given as ( -2, -1, 0, 1, 2 ). Just like the s – orbitals, with an increase in size and energy of p orbitals quantum number ( 4p > 3p > 2p ), the size and energy of p orbitals also increase.
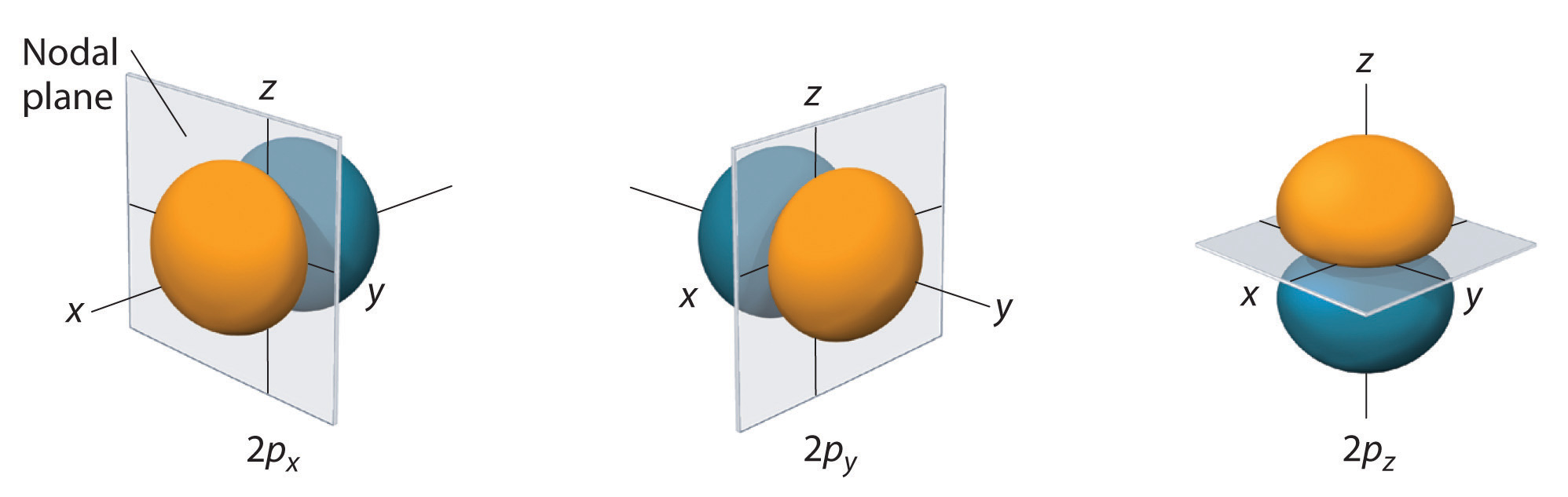
Therefore, we can say that there are about 3 p orbitals whose axes are mutually perpendicular. These lobes are placed along one of the x, y, z-axis and are given description 2px, 2py, and 2pz. However, they are very identical in terms of the size, shape, and energy. All the three p orbitals vary in the way of the orientation of the lobes. P – OrbitalsĮach p orbitals comprises of two sections referred to as lobes that lie on either side of the plane passing through the nucleus. With the increase in the value of a principal quantum number, say n, the size of the s orbital will also increase. The s – orbitals are spherically symmetric having the probability of finding the electron at a given distance equal in all the directions.
#The halogen with electrons in the 4p atomic orbitals download
You can download Structure of Atom Cheat Sheet by clicking on the download button belowĭetermination of Shapes of Atomic Orbitals S – Orbitalsįor the s orbital, the boundary surface diagram looks like a sphere having the nucleus as its centre which in 2 dimensions can be seen as a circle. Towards Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom.Development Leading to Bohr’s Model of Atom.How are Electrons Distributed in Different Orbits (Shells)?.For example – there is one orbital of s – a type of the value of I is 0, 3 p – orbitals of the value of I is one, 5 d – orbitals if the value of I is 2 and so on.īrowse more Topics Under Structure Of Atom The total permitted values of m for a given value of I to give the number of orbitals of one type within a subshell. This has been used to ascertain the spectral lines in the atomic spectra of different atoms. The symbols s, p, d, f originally comes from the words meaning sharp, principal, diffuse and fundamental respectively. Herein, the number is denoted by the level of energy of the electron in the orbital.ġ refers to the energy level that is closest to the nucleus, however, 2 refers to the next level of energy further out. Each of the orbitals is denoted by a number and a letter. In other words, orbitals are the regions of space in which electrons are usually to be found. The shapes of atomic orbitals and the orientation define that there is no probability of finding the electron along some certain directions than among others. An orbital which is of small size states that there is more chance of finding the electron near the nucleus. There are various shapes of atomic orbitals. In an atom, there are a large number of orbitals.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
